Isoelectric Point
Definition
Isoelectric point is a value of pH when zeta potential of the system equals 0. Stability of many dispersions and emulsions are often related to the pH of the solution. There is semi-empirical rule stating that system would be stable when its pH located beyond 2 pH units vicinity of the iso-electric point. Furthermore, ISO Standard 13099, Parts 1 and 3: 2012. Colloidal systems – Methods for Zeta potential determination provides definition of the iso-electric point.
Precision of the zeta potential measurement is critical for achieving the high accuracy of the isoelectric point determination. Consequently, Electroacoustic method has big advantage over other methods of zeta potential characterization. Precision of zeta potential measurements with models DT-310 and DT-1202 is ± 0.1 mV.
Verification
There was detail study of various methods suitable for characterizing iso-electric points conducted by international group: Hackley, V., Patton, J., Lum, L., Wasche, R.J., Naito, M., Abe, H., Hotta, Y., and Pendse, H. “Analysis of the Isoelectric Point in Moderately Concentrated Alumina Suspensions Using Electroacoustic and Streaming Potential Methods“, J. of Dispersion Science and Technology, 23, 5, 601-617 (2002)
Evidently, this study established that our instruments determine isoelectric point with accuracy of 0.1 pH unit.
Determination of the isoelectric point does not require calibration of the electroacoustic device. Phase of electroacoustic signal rotates 180 degrees at this pH value. Consequently, this is an absolute definition of the isoelectric point.
Examples
Figure below illustrates results of pH titrations for alumina slurry at 4% vl and rutile slurry at 7% vl.
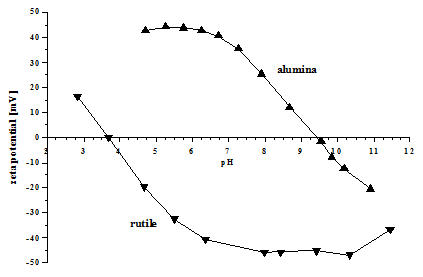
Titration
Generally, determination of isoelectric point requires automatic burettes. These devices are capable of injecting chemicals into the sample when it is stirred. Precision of the injection is 1 microliter. Software controls their functions according to the preliminary defined protocol. This protocol specifies minimum and maximum pH, number of points, direction of pH change.
Our Book on Ultrasound for characterizing colloids contains a separate chapter on titrations.
`
