ZETA POTENTIAL of POROUS MATERIAL
Introduction
Electroacoustics offers a unique possibility for characterizing zeta potential in both types of heterogeneous systems ( porous material and particulates ) with the same device. Model DT-330 is such Universal Zeta potential Probe since it can conduct such measurement for both types of dispersed systems. Model DT-1202 can conduct similar measurement when it has an Option OP0014.
The main principles of Electroacoustics in porous material are presented in ISO Standard 13099, Parts 1 and 3: 2012. Colloidal systems – Methods for Zeta potential determination.
Moreover, all details of these instruments are described in the US Patent by Dukhin, Goetz and Thommes from 2012 “Method for determining porosity, pore size and zeta potential of porous bodies”.
Method description
Zeta potential probe designed by Dispersion Technology Inc has a flat face. Therefore, it can be simply placed on the top of the porous body, as shown below with a sandstone core.

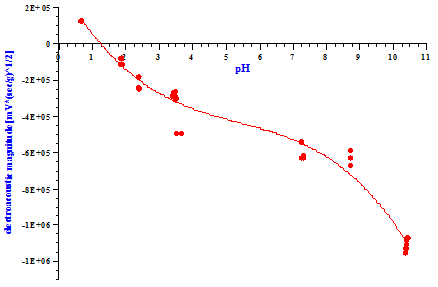
Further, we can change pH of the liquid that saturates porous material when observing how surface charge of the pores varies with pH. Consequently, Figure below shows such pH titration of Berea SS sandstone core.
Publications
Papers from the list below present some examples of these measurements:
-
-
Dukhin, A.S., Swasey, S. and Thommes M. “A method for pore size and porosity analysis of porous materials using electroacoustics and high frequency conductivity“, Colloids and Surfaces, 437, pp. 127-132 (2013)
-
Dukhin, A.S., Goetz, P.J., and Thommes M. “Seismoelectric effect.: A non-isochoric streaming current. 1. Experiment“, J. Colloid and Interface Science, 345, p.547-553 (2010)
-
Dukhin, A.S. and Shilov, V.N. “Seismoelectric effect.: A non-isochoric streaming current. 2. Theory“, J. Colloid and Interface Science, 346, p.248-253 (2010)
-
Dukhin, A.S. and Parlia, S. “ Studying homogeneity and zeta potential of membranes using electroacoustics “, J. of Membrane Science, vol. 415-415, pp. 587-595 (2012)
-
Meanwhile, our book contains a full review.
Furthermore, calculation of zeta potential requires information on porosity. Conductivity probe of DTI instrument offers such porosity measurement since it functions at 3 MHz frequency and not affected by electrode polarization. Measured “form factor” is a source of information for calculating porosity when Maxwell-Vagner theory applied. Consequently, DTI provides full set of tools for measuring zeta potential in porous bodies.
